Greetings from the world of First Person View (FPV) drones! Below, we’ve outlined everything you need to know about FPV drones. Whether your goals are freestyle flying, racing, or just seeing the sky from a different angle, this course will give you insightful knowledge and useful pointers to get you started. We can help you with anything from comprehending the fundamentals and choosing the appropriate fpv drone parts to learning safe flying techniques and maximising the capabilities of your drone.
Together, let’s take off on this thrilling journey to explore the countless opportunities presented by FPV drone flight! Additionally, if you want to buy FPV parts or FPV drone kits, Buy them at MEPSKING drone shop.
What is FPV Drone?
The acronym for first person view is FPV.
A drone with a camera that broadcasts live video to goggles worn by the pilot is known as an FPV drone. The operator can operate the drone while on the ground by using this real-time “first-person” view, much like if they were in the cockpit. You can have an immersive experience by wearing goggles to fly an FPV drone and see the world via the drone’s eyes.
Because of an FPV drone’s speed and agility, flying one demands a great deal of concentration, but the experience is genuinely amazing. When operating an FPV drone, the pilot uses a remote controller with joysticks for flight control while donning goggles to view the live video feed from the drone’s camera. It’s similar to playing a video game, but instead of winning, you lose real-world points, like breaking an expensive first-person shooter drone!
While some FPV drone pilots fly for a living (racing, filming, etc.), most do it as a pastime on their days off. The FPV drone community is friendly and energetic, fostering connections and knowledge sharing among like-minded people.
What is the Difference between FPV and Normal Drones?
FPV drones differ from normal drones primarily in the perspective and control experience they offer. While normal drones are piloted based on line-of-sight or through a smartphone/tablet screen displaying the drone’s camera feed.
FPV drones provide a more immersive flying experience by streaming live video from the drone’s camera directly to goggles or a headset worn by the pilot. This allows for a first-person view as if the pilot is in the cockpit of the drone, enabling more precise maneuvers, especially in drone racing or aerial cinematography.
if you want to have fun piloting, then FPV drones are the best choice. On the other hand, if you want a hassle-free flying experience and peace of mind, then stabilized drones are the way to go.

What are the Types of FPV Drone?
In order to get started with FPV, you have to understand what types of FPV drone. FPV drones are categorized based on their flying style, functionality, and size to meet the diverse needs of enthusiasts and professionals. In brief, these drones can be classified into the following categories:
Based on Flying Style/Functionality

- Tiny Whoop: Known for their protective ducts around the blades, they are suitable for indoor flying and beginners.
- Cinewhoop: Usually larger than 2.5 inches, with wider and thicker ducts, designed for high-definition aerial photography.
- FPV Racing Drones: The 5-inch model is the most common for racing, fitting for competitions, freestyle performances, or high-definition aerial photography.
- Toothpicks: Named for their thin arms, they are designed for speed and agility.
- Long-range: Specifically used for long-distance aerial photography, featuring slender bodies and large-capacity batteries.
Based on Size

- Small: Utilizing propellers with diameters less than 4 inches, mainly for indoor or low-wind conditions.
- Medium: With 4 to 6 inches propellers, this is the most common FPV drone size, suitable for various flying styles.
- Large: Using propellers larger than 7 inches, primarily for long-distance flying and professional-grade aerial photography.
Additionally, the market also offers pre-assembled drone kits such as RTF (Ready-to-Fly) and BNF (Bind-and-Fly) to accommodate pilots of different skill levels.
Understanding these classifications not only helps flying enthusiasts and professionals to select the appropriate FPV drone but also ensures that they can achieve the best flying experience according to their flying goals and preferences. Whether seeking the thrill of speed or enjoying serene aerial photography, FPV drones provide a unique perspective and flying joy.
What are Parts of FPV Drone?
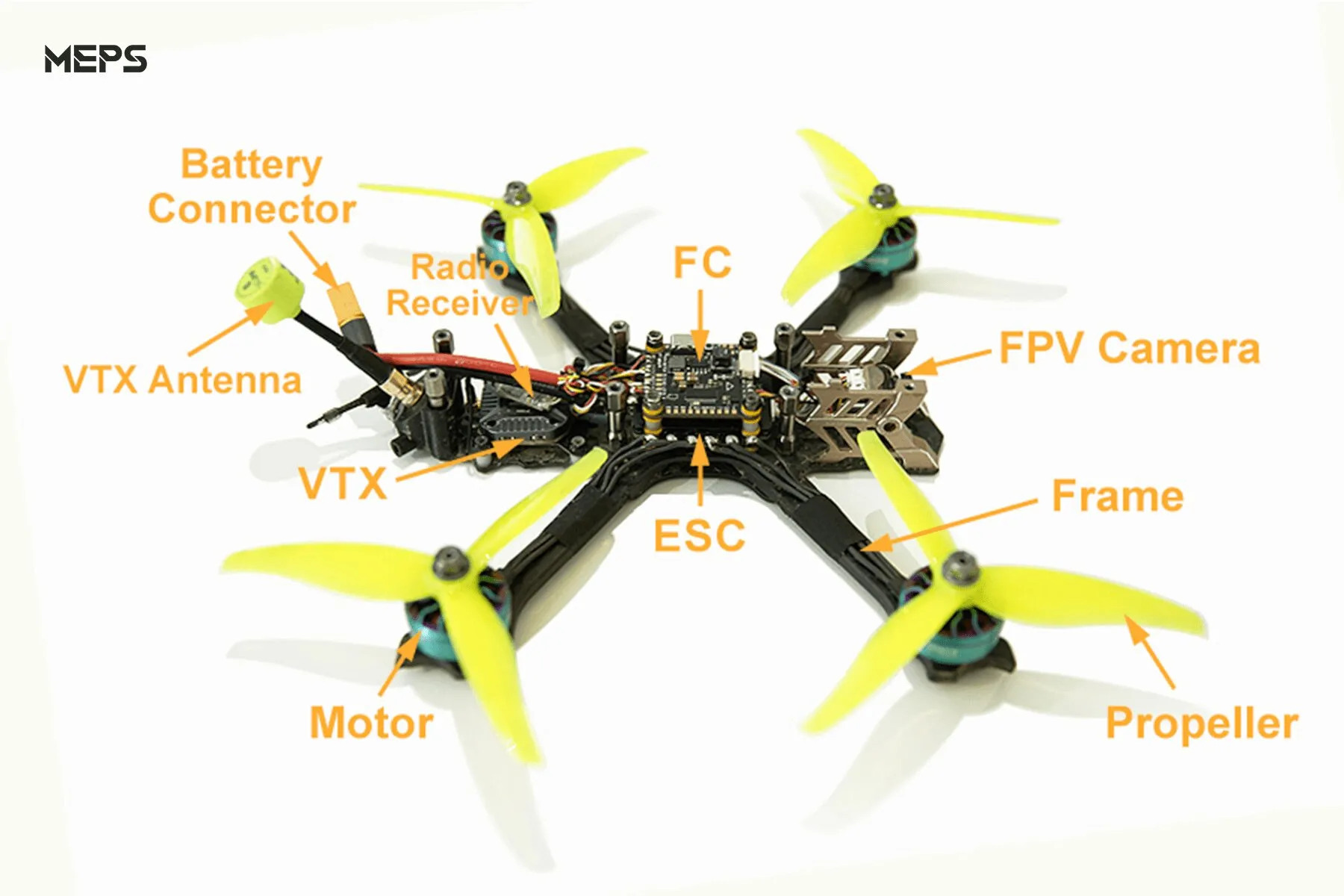
To become a skilled FPV pilot, you first need to understand the key parts of FPV drone, ensuring you can fly safely and enjoy an unparalleled visual experience. In this course, you’ll learn about the core building blocks of a drone, such as flight controllers, motors, propellers, and batteries, and how to select and configure them to suit your needs and flying style. We’ll also dive into the video delivery system and how to achieve realistic FPV images and video streaming, allowing you to achieve stunning visuals on the fly.
FPV (First Person View) drones offer an immersive flying experience, facilitated by a combination of specialized components. These components are categorized into three main systems: the flight system, power system, and FPV system.
- Flight System: This includes FPV motor, drone propellers, electronic speed controller for drone (drone ESC), flight controller, and a radio receiver. These components ensure the drone’s maneuverability and stability during flight.
- Power System: Comprising a battery and a power distribution board, this system provides the necessary power to all the drone’s components, particularly influencing flight time and performance.
- FPV System: Central to the FPV experience, this system consists of a FPV camera, FPV antenna, video transmitter (FPV VTX), and sometimes, a recording device like a GoPro. It transmits live video from the drone to the pilot’s goggles or screen, allowing for a first-person flying perspective.
When building an FPV drone, choosing the right parts is crucial for optimal performance. Important considerations include the weight, expected flight time, and environmental conditions for the frame; motor efficiency and power; battery voltage, capacity, and discharge rate; and camera quality and transmission distance for the FPV system.
FPV System
As briefly mentioned above, the FPV system comprises a camera, an antenna, a video transmitter and a video receiver. And there are two great FPV systems in the market:
- Analog FPV System
- Digital FPV System(HD)
Analog FPV System
Advantages:
Cost-Effective: Cameras and VTX range from $12 to $40.
Versatile: Compatible with various drone types and sizes.
Compatibility: Mix and match components from different manufacturers.
Good Signal Penetration: Effective in indoor and forest environments.
Low Latency: Quick response time, ideal for speed and recovery.
Disadvantages:
- Low Video Quality: Maximum resolution is 576p (PAL) or 480p (NTSC).
Digital FPV System
Brands: DJI, WalkSnail, HDZero
Advantages:
- High Video Quality: Resolutions up to 1080p at 100fps.
- Support and Warranty: Better support and easier maintenance.
- Latest Technology: Constant updates and improvements.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost: Initial setup and maintenance are more expensive.
- Lower Penetration: Generally less effective in indoor environments.
- Video Noise Issues: Different handling of noise, with potential for image freezing or blackouts.
Recommendation:
- Analog: Ideal for beginners and those on a budget.
- DJI: Best for high-quality, stable flights.
- HDZero or WalkSnail: Great for versatile flying needs, with specific strengths in racing (HDZero) or general use (WalkSnail).
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of BNF RTF PNP DIY FPV Drone?
For the first time, you wish to purchase the fpv drone. You will rapidly see these acronyms next to the drones: PNP, BNF, RTF. Here, we’ll explain what are the differences between BNF RTF PNP and DIY fpv drone.
The article explores the decision-making process between purchasing a pre-build FPV drone kit or building one from scratch. It explains the meaning of acronyms such as BNF, RTF, PNP, and DIY, and delves into the advantages and disadvantages of each option. Whether one chooses convenience and instant readiness with prebuilt kits or opts for customization and learning opportunities with a DIY approach, the article provides insights to help readers make an informed decision. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of seeking advice from experienced pilots and highlights the different considerations for beginners and experienced users in the FPV drone hobby.

How Much does an FPV Drone Cost?

Embarking on the thrilling adventure of FPV drone flying brings excitement and opportunity, but understanding the financial investment involved is essential for enthusiasts at all levels. From beginners exploring RTF kits to experienced pilots customising their DIY builds, the cost of FPV drones varies widely. Here we’ll look at the intricacies of FPV drone costs, exploring different types of drones, build versus buy considerations, key cost factors and additional expenses.
Understanding the cost of FPV drones is crucial for enthusiasts at all levels. Here’s a breakdown of the key points to consider:
Types of FPV Drones
- Ready-to-Fly (RTF) kits: Ideal for beginners, priced around $200 to $500.
- Pre-built quads: Suitable for intermediate users, priced between $300 to $600.
- DIY builds: Offers customization, costs range from $400 to $1,800 depending on parts.
Building vs. Buying
- Building your own drone offers customization and skill development.
- Buying pre-built drones saves time and may be more suitable for those focused on flying.
Cost Factors
- Basic parts: Frame ($20-$150), Flight Controller ($20-$200), ESC ($50-$250), Motors ($20-$50 each), Propellers ($2-$15), Batteries & Charger ($20-$100 each), Video Transmitter ($20-$200), FPV Camera ($30-$100).
- Other parts: Radio Transmitter & Receiver ($50-$300), FPV Goggles ($100-$700), Tools ($100), FPV Simulator ($0-$30), Maintenance/Repair, Upgrades.
Additional Expenses
- FPV simulator: Essential for skill development, costing $0 to $30.
- Maintenance/Repair: Inevitable costs for damaged parts.
- Upgrades: Adding accessories for improved performance, such as FPV goggles or cameras.
Understanding these cost factors helps enthusiasts budget effectively and make informed decisions when building or buying FPV drones. By weighing the options and considering individual preferences and skill levels, enthusiasts can embark on an exciting FPV journey while managing costs effectively.
What Skills are Required for FPV Flying?
Drone flying using First-Person View (FPV) technology is an exciting pastime that lets you enjoy the rush of flight and see the world from a different angle. This in-depth book will walk you through the fundamental skills and procedures that every FPV drone pilot should be able to do, regardless of your level of experience. We will cover every aspect of FPV flying, from the fundamentals to more complex manoeuvres, to help you become an expert and self-assured pilot.
If you want to become an FPV pilot,the basic skils that everyone needs to master.

Technical Understanding
Knowledge of drone components and mechanics, including how to assemble a drone, understanding the function of each part (such as motors, ESCs, cameras, and antennas), and the basics of electrical systems.
Manual Dexterity and Coordination
The ability to control the drone’s movements accurately via the remote controller. This involves precise thumb or finger movements on the joysticks to control the drone’s pitch, roll, yaw, and throttle.
Line Of Sight Flying
When a drone is flying in line of sight (LOS), you are operating it by looking straight at it rather than through FPV goggles or a display.
It’s best to have some LOS flying experience before diving right into FPV. This is helpful since it allows you to securely land and control your drone even if you lose video signal.
It’s not necessary to acquire complex manoeuvres; the most important thing is to ensure that you can stabilise the quad and manoeuvre it throughout the field without becoming lost.
It’s crucial that you face forward while standing behind the quad and beginning your practice. This makes it simpler and more natural for you because it will enable your quad to move in the same direction in response to your transmitter sticks.
Quick Reflexes and Decision-Making
FPV flying often requires rapid responses to unexpected situations, such as avoiding collisions or handling sudden wind gusts. Pilots must make split-second decisions to maintain safety and course.
Spatial Awareness
Being able to judge distances and spatial relationships between objects from the drone’s perspective. This skill is crucial to navigate through tight spaces or around obstacles.
How to Practice FPV Drone in Simulator?
FPV drone simulator is a software that simulates flight controllers and drones, allowing users to simulate the flying experience of drones in a virtual environment, thus helping drone enthusiasts to practice their flying skills, test different controller settings, evaluate aircraft performance and test flight sites, etc.
We will discusses various FPV (First Person View) drone simulators, which are software tools that simulate the experience of flying drones in a virtual environment. It lists several popular simulators such as DRL (Drone Racing League) Simulator, Liftoff, Velocidrone, and others, highlighting their features, pros, and cons. These simulators are designed to help beginners and enthusiasts improve their flying skills, test flight controllers, and evaluate drone performance in various scenarios. We will also covers considerations for choosing the right simulator based on purpose, features, operation, cost, and compatibility. Additionally, it provides download links and pricing for each simulator, making it easier for users to access and evaluate them.
Where to Find the FPV Communities and Resources?
Finding the FPV (First Person View) drone flying community and accessing resources can greatly enhance your flying experience and skill development. Here are some good places to start.
Online Forums and Communities
- RCGroups: This is one of the largest forums for RC hobbyists with a dedicated section for FPV enthusiasts. You can find discussions on everything from beginner tips to advanced technical modifications.
- FPVLab: Another focused FPV forum where users share builds, video footage, and technical advice.
- Reddit: Subreddits like r/fpv, r/Multicopter, and r/drones are active communities for sharing news, tips, and project ideas.
- intoFPV: Never hesitate to get in touch if you need help or direction. Post a remark below, conduct an online search, or register forthis forum. You can progress and save money by speaking with seasoned pilots and having them check your components list before placing an order.
Educational Resources and Tutorials
Websites like Oscar Liang or Joshua Bardwell’s YouTube channel offer in-depth tutorials, equipment reviews, and practical tips for FPV pilots.
FPV Racing and Freestyle Events
Attending FPV racing and freestyle competitions is a great way to meet other enthusiasts and see different flying styles and setups. These events often feature vendors and workshops.
Online Retailers and Manufacturers
Many FPV gear manufacturers and online retailers maintain blogs, support forums, and learning centers on their websites. Examples include MEPSKING, GetFPV, RaceDayQuads, and Banggood’s FPV section. These platforms often provide tutorials, product reviews, and guides that can be very helpful for both new and experienced pilots.
How to Improve FPV Drone Performance?

By Soldering & Tuning
Enhancing your FPV drone’s performance starts with clean wiring and proper soldering. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced pilot, optimizing your build ensures better flight stability, responsiveness, and overall efficiency.
Best ESC & FC Soldering Tips
- Use a Practice Board – If you’re new to soldering, start with a practice board to avoid damaging components.
- Choose Quality Solder – 0.8mm 60/40 Rosin-Cored Solder offers strong, reliable joints.
- Secure Motor Wires – Use tape or wire shields to prevent damage and reduce vibrations.
- Organized Wiring – Twist wires to minimize electrical noise and avoid routing them over the gyro chip.
Optimizing Flight Performance
- Rubber Gummies – Prevent excess vibrations by ensuring a secure yet flexible flight controller mount.
- Reduce Video Feed Noise – Twist wires or install an LC filter for cleaner analog video transmission.
- Set the Right VTX Channel – Manually tune your video transmitter to avoid signal loss mid-flight.
Betaflight PID Tuning
- Adjust PID Settings – Fine-tune responsiveness and stability based on your drone’s setup.
- Use Presets – The Betaflight preset tab offers optimized tunes for racing, freestyle, and cinematic flying.
For a detailed guide on improving your FPV drone’s performance, check out Improving FPV Drone Performance by Soldering & Tuning Tips!.
FAQs
Here are the F&Q section of fpv drone.
How High Can Drones Fly?
Most consumer-grade drones, like those from DJI, are typically capable of flying up to 500 meters (about 1,640 feet) above the ground level. However, they are often limited by software to lower altitudes to comply with local regulations. Above 1,000 feet, lightweight consumer drones might not perform well.
- In the United States: Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulations restrict drones to a maximum altitude of 400 feet while in flight. Special authorizations are required for flights over this altitude. In addition, the drone model, weight, weather, and other factors affect the maximum altitude.
- Europe (EASA Regulations): Similar to the FAA, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) also sets a general limit of 120 meters (about 394 feet) for drone operations, unless specific permissions are obtained.
What is the Maximum Speed of an FPV Drone?
How quickly then do drones fly? Yes, there is a simple answer to this: it depends on the various applications—be they for consumer, military, or racing—that call for particular speeds. Here are the Speed Ranges of different fpv drone types.
- Racing Drones: These are built for speed and agility, and can typically reach speeds of 80-100 miles per hour (mph) or about 130-160 kilometers per hour (km/h). Some custom-built racing drones have been recorded to reach speeds over 120 mph (193 km/h).
- Freestyle and Consumer Drones:While not as fast as racing drones, freestyle drones, which are built for maneuverability and aerial acrobatics, typically reach speeds of 40-60 mph (64-97 km/h). Consumer drones, which are designed for general photography and videography, usually have lower maximum speeds, around 35-50 mph (56-80 km/h).
What Makes an FPV Drone Faster?

If you’re considering purchasing a speedier model, you should be aware of the following things that affect their pace and accelerate them:
- The drone’s speed is largely determined by the motor and propeller power and efficiency. More thrust is produced by high-performance propulsion systems for faster acceleration.
- Drones can travel through the atmosphere more quickly thanks to a sleek and aerodynamic design that lowers air resistance.
- Drones that are lighter can travel faster since they need less energy to do so. Therefore, construction materials are important when it comes to managing weight.
- Even at great speeds, control must be maintained via sophisticated flight controllers and stability devices. They are essential to a drone’s speed since they guarantee a steady and safe flying experience.
- The duration of high-speed flying for a drone is determined by its battery’s efficiency and capacity. Batteries with a longer lifespan offer the stamina required for quicker flights.
Knowing these important variables demonstrates how well they work together to enable a drone to reach remarkable speeds. A well-balanced model has minimal weight, powerful propulsion, a sleek design, sophisticated control systems, and effective batteries.
What are the Law Requirements and Safety Issues with FPV Flying?

Flying FPV drones offers an exhilarating experience that blends technology with the thrill of flight. However, navigating the skies with these sophisticated devices is not just about fun and excitement; it also demands a keen understanding of legal frameworks and stringent adherence to safety protocols. In the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) sets forth clear guidelines that every drone enthusiast must follow to ensure safe and lawful operations. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the law Requirements and Safety Issues In FPV Flying. From registration and certification to understanding no-fly zones and managing flight risks, we’ll cover everything you need to know to enjoy your flying experience while complying with the regulations.
Do You Need a License to Fly an FPV Drone?

Flying FPV drones in the United States involves a blend of excitement and responsibility. As this technology becomes more accessible and its applications broaden, understanding the legal requirements, particularly those enforced by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), is crucial for operators.
Do you need a license to fly FPV in US? This is a question that has always bothered FPV beginners. While recreational flyers don’t need an FAA license, commercial operators must obtain a Remote Pilot Certificate under Part 107. Additionally, using ham radio frequencies requires a Technician Class license from the FCC. Although some FPV systems operate under Part 15 certification, accessing higher power modes demands a ham license. With a ham license, pilots enjoy better communication, range, and legal compliance. Obtaining a Technician Class license involves passing an exam covering regulations and electronics theory. Understanding and following these licensing requirements ensure safe and enjoyable FPV drone flying experiences in the US.
Can You Take Drone on a Plane?
It can be a fantastic idea to take drone on a plane for your travels in order to take some incredible pictures of your family or to record a breathtaking landscape. There are other restrictions to take into account, though. You can feel more at ease with the aid of our guide.
You can take a drone on a plane, but there are specific regulations you need to follow, primarily concerning the drone’s batteries, which are subject to airline and international aviation regulations due to their potential fire hazard.

How to Waterproof FPV Drones?
An FPV drone’s electronics must be waterproofed in order to extend its lifespan, and conformal coating is the most popular technique for doing so. You can make sure your drone can fly in harsh weather by shielding its parts from moisture and chemical deterioration after waterproofing FPV drones.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide on how to waterproof FPV drones using silicone conformal coating to protect their electronics from moisture and water damage. It covers the types of waterproofing materials, the importance of waterproofing for FPV drones, and detailed steps for applying and removing conformal coating. Key points include preparing the drone, applying the coating to critical components without obstructing essential parts, checking for complete coverage, and drying. Additionally, it offers advice on what to do if the drone crashes into water and emphasizes the necessity of waterproofing to enhance the drone’s durability and performance in various environmental conditions.

How to Match the FPV Motor and Battery for Your Drone
One of the most important steps in creating and perfecting your FPV is matchinging the proper motors and batteries for your drone. The cooperation between the battery and motor greatly affects your drone’s mobility, endurance, and performance. You may optimize the performance of your drone and attain a remarkable flying experience by being aware of the many factors to take into account when choosing components.
The drone’s total weight, the amount of thrust needed, and the desired flying style should all be taken into consideration when selecting a motor. In general, brushless motors are more powerful and have higher efficiency than brushed motors; however, size and Kv must be carefully chosen to meet the particular requirements of your project.
The battery’s nominal voltage, capacity, and discharge rate are important factors to take into account. Aggressive movements can be powered by a high-quality LiPo battery with a rapid discharge rate, all without sacrificing battery life. For the best flying performance, select a battery that delivers the ideal ratio of weight to capacity and that corresponds with the specifications of your motor.
Finally, keep in mind how crucial safety is when utilizing LiPo batteries. Always abide by recommended procedures for handling, charging, and storing items to reduce the chance of an explosion or fire.
